The AI Brain - Neural Networks Demystified
Updated: October 28, 2025
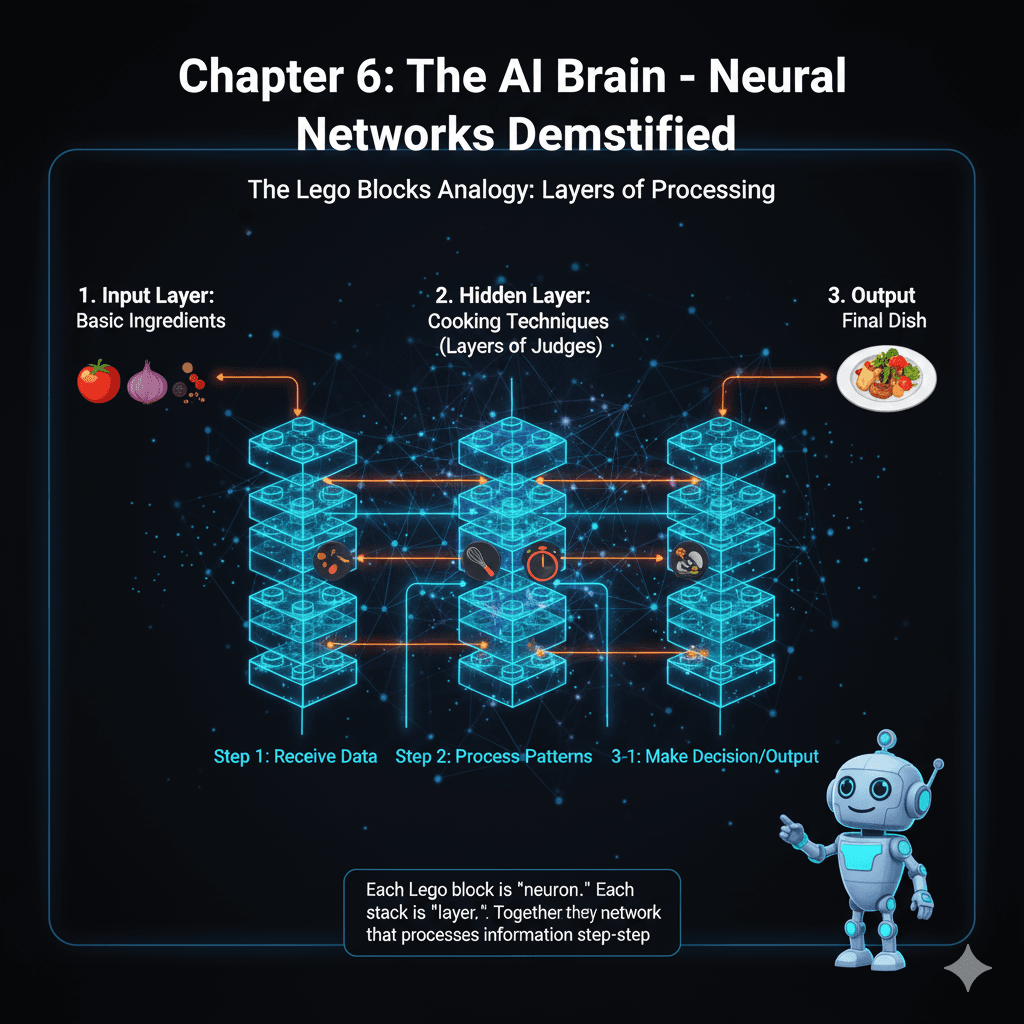
Neural networks are like building with Lego blocks. Just as you can build anything with enough Lego blocks, neural networks can learn any pattern with enough neurons.
Let me show you how these building blocks connect to create AI's brain.
🧱The Lego Block Analogy
Single Block = One Neuron
Processes simple information
Stack of Blocks = Layer
Processes complex patterns
Entire Structure = Neural Network
Solves complex problems
A Neuron: The Basic Building Block
Think of a neuron like a judge in a talent show:
Talent Show Judge
- 1.Watch each act (receive inputs)
- 2.Score each act (apply weights)
- 3.Add up scores (sum)
- 4.Decide: "Yes" or "No" (output)
In AI Terms
Layers: Teams of Neurons
Imagine a cooking competition with multiple rounds:
Round 1: Input Layer (Basic Ingredients)
- • Judge 1: Evaluates freshness
- • Judge 2: Evaluates quality
- • Judge 3: Evaluates variety
Round 2: Hidden Layer (Cooking Techniques)
- • Judge 4: Takes Round 1 scores, evaluates preparation
- • Judge 5: Takes Round 1 scores, evaluates seasoning
- • Judge 6: Takes Round 1 scores, evaluates cooking time
Round 3: Output Layer (Final Dish)
- • Judge 7: Takes all previous scores, makes final decision
This is exactly how neural networks process information - layer by layer, with each layer building on the previous one.
Deep Learning: Many Layers Deep
"Deep" learning just means many layers:
Simple Network (Shallow)
Like: Deciding if email is spam
Deep Network
Like: Recognizing faces in photos
The more layers, the more complex patterns:
- • 2 layers: Simple patterns (lines, edges)
- • 5 layers: Complex shapes (circles, squares)
- • 10 layers: Objects (faces, cars)
- • 50+ layers: Abstract concepts (emotions, style)
Training: The Learning Process
Let's train a network to recognize hot dogs:
Step 1: Random Start
Step 2: Getting Warmer (After 100 images)
Step 3: Almost There (After 1,000 images)
Step 4: Expert (After 10,000 images)
The Magic of Backpropagation (Explained Simply)
When the network makes a mistake, it needs to figure out which neurons were wrong. It's like detective work:
🔍Detective Investigation
Real-World Example: Reading Handwritten Numbers
Let's see how a network reads your handwriting:
Input Layer (784 neurons - one per pixel in 28×28 image)
Sees: Pixel brightness values
"Is this pixel black or white?"
Hidden Layer 1 (128 neurons)
Learns: Edges and lines
"I see a vertical line here, curve there"
Hidden Layer 2 (64 neurons)
Learns: Shapes
"That's a circle on top, line at bottom"
Output Layer (10 neurons - one per digit 0-9)
Decision: Which number?
Types of Neural Networks (With Real Examples)
1. Feedforward (Basic)
2. Convolutional (CNN)
3. Recurrent (RNN)
4. Transformer
The Power of Activation Functions (The Personality)
Activation functions give neurons "personality":
Linear (boring)
"I just pass along what I'm told"
ReLU (optimistic)
"I only share positive news"
Sigmoid (decisive)
"It's definitely yes or no"
Tanh (balanced)
"I consider both positives and negatives"
Different personalities for different tasks!
Build Your Own "Neural Network" (Paper Exercise)
The Ice Cream Predictor Network
Goal: Predict if someone will buy ice cream
Inputs (Rate 0-10):
- 1. Temperature outside
- 2. Day of week (1=Monday, 7=Sunday)
- 3. Money in pocket
Hidden Layer (Your rules):
- • Neuron 1: If temp > 7 AND money > 5 → Likely
- • Neuron 2: If weekend AND money > 3 → Likely
- • Neuron 3: If temp < 3 → Unlikely
Output:
If 2 or more neurons say "Likely" → Predict: Will buy ice cream!
Try it with real scenarios:
- • Hot Saturday (temp=9), $10 → Buy? (Yes!)
- • Cold Tuesday (temp=2), $2 → Buy? (No!)
Congratulations! You just simulated a neural network!
🎓 Key Takeaways
- ✓Neural networks are like Lego blocks - simple pieces create complex systems
- ✓Neurons are judges - they score inputs and make decisions
- ✓Layers process information sequentially - each layer builds on the previous
- ✓Deep learning = many layers - more layers learn more complex patterns
- ✓Training adjusts weights through repetition - learning from mistakes
- ✓Backpropagation traces errors backwards - finding what went wrong
- ✓Different network types for different tasks - CNN for images, RNN for sequences, Transformer for language
❓Frequently Asked Questions
How do neural networks work in simple terms?
Neural networks work like Lego blocks - each neuron is a simple decision-maker that processes information, and when you connect many neurons in layers, they can learn complex patterns. Each neuron receives inputs, applies weights (like importance scores), sums them up, and makes a decision. Multiple layers process information sequentially, with each layer building on the previous one's understanding.
What is backpropagation in neural networks?
Backpropagation is how neural networks learn from mistakes. When the network makes an incorrect prediction, it works backwards from the error to figure out which neurons contributed most to the mistake. It's like detective work - the output layer blames the hidden layers, which blame earlier layers, until each neuron knows how much to adjust its weights to do better next time. This process repeats thousands of times until the network becomes accurate.
What are the main types of neural networks?
The four main types are: 1) Feedforward networks - basic one-way processing for simple tasks like spam detection, 2) Convolutional Neural Networks (CNN) - designed for images, used in face recognition and medical imaging, 3) Recurrent Neural Networks (RNN) - have memory for sequential data like text or time series, used in predictive text, and 4) Transformers - process everything in parallel, advancing language understanding in models like ChatGPT.
Why is deep learning called 'deep'?
Deep learning is called 'deep' because it uses many layers of neurons (hence 'deep' architecture). While simple neural networks might have 2-3 layers, deep networks can have 10, 50, or even hundreds of layers. Each layer learns increasingly complex patterns - early layers learn simple features like edges or basic patterns, middle layers combine these into shapes or concepts, and final layers recognize complete objects or abstract ideas. More layers allow the network to learn more sophisticated patterns.
What do activation functions do in neural networks?
Activation functions give neurons 'personality' by deciding how they respond to inputs. They transform the neuron's weighted sum into an output signal. Common types include: ReLU (only passes positive values, like an optimistic neuron), Sigmoid (squashes output to 0 or 1, like a decisive neuron), Tanh (outputs between -1 and 1, like a balanced neuron), and Linear (passes input through unchanged). Different functions work better for different tasks, helping the network learn different types of patterns.
🔗Authoritative Neural Network Resources
📚 Research Papers & Pioneering Work
Learning Representations by Back-Propagating Errors
Rumelhart, Hinton & Williams (1986)
The foundational paper that introduced backpropagation algorithm
ImageNet Classification with Deep Convolutional Neural Networks
Alex Krizhevsky et al. (2012)
The AlexNet paper that advanced deep learning for computer vision
Attention Is All You Need
Vaswani et al. (2017)
The Transformer architecture paper that advanced NLP
🛠️ Educational Resources & Tools
TensorFlow Playground
Interactive neural network visualization tool by Google
CS231n: Deep Learning for Computer Vision
Stanford's comprehensive course on neural networks and CNNs
DeepLearning.AI Neural Networks Guide
Andrew Ng's comprehensive neural network educational resource
PyTorch Neural Networks Tutorial
Hands-on tutorial for building neural networks with PyTorch
💡 Educational Tip: These resources provide deeper technical understanding for those who want to explore neural networks beyond the Lego analogies. Start with TensorFlow Playground for interactive learning, then explore the research papers as you advance.
🎓Educational Information & Learning Objectives
📖 About This Chapter
Educational Level: High School to College Beginner
Prerequisites: Basic computer literacy, curiosity about AI
Learning Time: 17 minutes (plus hands-on exercises)
Last Updated: October 28, 2025
Target Audience: AI enthusiasts, students, professionals new to neural networks
👨🏫 Author Information
Content Team: LocalAimaster Research Team Education Team
Expertise: Neural network architecture, deep learning pedagogy, AI education
Educational Philosophy: Making complex AI concepts accessible through analogies and hands-on learning
Experience: 10+ years in AI education and curriculum development
🎯 Learning Objectives
📚 Academic Standards
Computer Science Standards: Aligned with AP Computer Science Principles
Mathematical Concepts: Basic algebra, logical reasoning
Critical Thinking: Problem-solving, pattern recognition, systems thinking
Technical Literacy: Understanding AI systems and their applications
🔬 Educational Research: This chapter incorporates research-based learning strategies including analogical reasoning (Lego comparisons), hands-on simulation exercises, and scaffolding of complex concepts. The approach follows constructivist learning theory, building understanding from simple to complex neural network concepts.
Was this helpful?
Related Guides
Continue your local AI journey with these comprehensive guides
Ready to Build Your Own Dataset?
In Chapter 7, discover how to create training data for AI. Learn from a real 77,000 example journey!
Continue to Chapter 7