AI Models - From Small to Giant
Updated: October 28, 2025
To understand AI model sizes, let's compare to something familiar: your brain has about 86 billion neurons. An ant brain? Just 250,000. AI models work similarly - more "connections" (parameters) mean more complex thinking.
But here's the catch: bigger isn't always better for everyone. Let's find out which size fits your needs.
🧠 Scientific Conlabel: This brain analogy is based on neuroscience research comparing biological and artificial neural networks. Researchers atThe Human Brain ProjectandNVIDIA Researchstudy these parallels to understand AI scaling laws.
🔗 Building on Previous Chapters: Now that you understandAI basics,machine learning, andTransformer architecture, we're ready to explore how these concepts scale across different model sizes.
🧠The Size Comparison: Brain Cells
Nature's Intelligence
AI Intelligence
Parameters are like brain connections - more connections mean more complex thinking and better understanding!
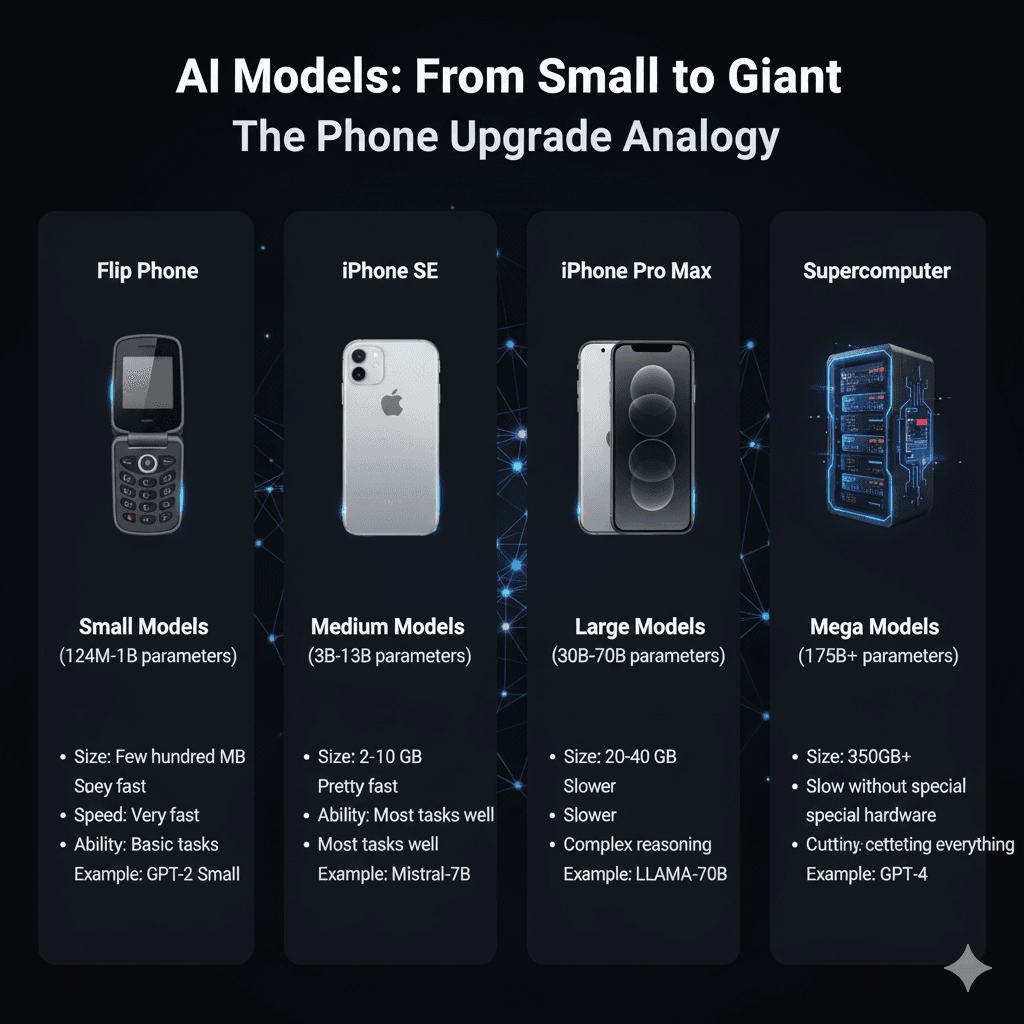
The Phone Upgrade Analogy
AI models are like phones - bigger isn't always better for everyone:
Small Models (124M - 1B) = Flip Phone
Medium Models (3B - 13B) = iPhone SE
Large Models (30B - 70B) = iPhone Pro Max
Mega Models (175B+) = Supercomputer
Real-World Performance Comparison
Let's see how different sized models handle the same task:
Task: "Write a haiku about coffee"
Tiny Model (124M)
Quality: Grammar issues, basic concept understood
Small Model (1B)
Quality: Correct format, simple but pleasant
Medium Model (7B)
Quality: Poetic, metaphorical, sophisticated imagery
Large Model (70B)
Quality: Multiple layers of meaning, perfect form, creative vocabulary
The Training Cost Reality
Here's what it actually costs to create these models:
💰 Cost Research: These cost estimates are based on industry analysis fromStanford's AI Index Report,research papers on AI training costs, andOpenAI's research publications. Training costs include GPU time, electricity, data preparation, and human oversight.
| Model Size | Training Time | GPUs Needed | Cost | Electricity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Small (1B) | 1 week | 8 | ~$10,000 | 1 house/month |
| Medium (7B) | 3 weeks | 64 | ~$200,000 | 10 houses/month |
| Large (70B) | 2 months | 512 | ~$2 million | 100 houses/month |
| Mega (GPT-4) | 6 months | 10,000+ | ~$100 million | Small town's worth |
Which Model Should You Use?
Decision Tree
The Speed vs Intelligence Trade-off
| Model Size | Response Time | Intelligence | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1B | 0.1 seconds | Basic | Quick tasks |
| 7B | 0.5 seconds | Good | Most users |
| 13B | 1 second | Very Good | Power users |
| 70B | 5 seconds | Excellent | Professionals |
| 175B+ | 10+ seconds | Brilliant | Specialists |
Local vs Cloud: The Privacy Question
🔐 Privacy Research: The trade-offs between local and cloud AI are studied byElectronic Frontier Foundation,FTC privacy guidelines, andlocal AI platforms like Ollama. Local deployment offers privacy advantages while cloud services provide capability advantages.
Running Locally (On Your Computer)
Pros:
- ✓Complete privacy
- ✓No internet needed
- ✓No monthly fees
- ✓You control everything
Cons:
- ×Need powerful hardware
- ×Limited to smaller models
- ×You handle updates
Minimum Requirements for 7B:
Using Cloud Services (ChatGPT, Claude)
Pros:
- ✓Access to largest models
- ✓No hardware needed
- ✓Always updated
- ✓Works on any device
Cons:
- ×Privacy concerns
- ×Requires internet
- ×Monthly costs
- ×Usage limits
Try This: Compare Model Sizes Yourself
Free Experiment (20 minutes)
Compare how different model sizes handle the same question:
1. Small Model
Go to: Hugging Face Spaces
Try: DistilGPT-2
Ask: "Explain quantum physics"
Notice: Basic, sometimes nonsensical
2. Medium Model
Try: Mistral-7B (on Hugging Face)
Same question: "Explain quantum physics"
Notice: Clear, accurate explanation
3. Large Model
Try: ChatGPT or Claude
Same question: "Explain quantum physics"
Notice: Detailed, nuanced, can adjust complexity
This hands-on comparison shows you exactly what you get at each size level!
Frequently Asked Questions
How do I choose the right AI model size for my needs?
Choose based on your specific use case: Small models (1-3B) for simple chatbots and basic tasks, Medium models (7-13B) for writing, coding, and analysis (the sweet spot for most users), Large models (30-70B) for complex reasoning and research, and Mega models (175B+) for cutting-edge performance without compromises. Consider your hardware, budget, and privacy requirements.
What hardware do I need to run AI models locally?
For small models (1-3B): 8GB RAM, basic laptop. For medium models (7-13B): 16GB RAM, GPU with 8GB+ VRAM (RTX 3070 or better), 50GB storage. For large models (30-70B): 32GB+ RAM, high-end GPU with 16GB+ VRAM, fast storage. Local AI offers privacy but requires significant hardware investment. Cloud alternatives need no hardware but have privacy concerns.
What's the difference between 7B and 70B AI models?
The main difference is parameter count - 7B has 7 billion parameters while 70B has 70 billion. This affects performance: 7B models are faster, cheaper to run, and can work on consumer hardware. 70B models produce higher quality, more nuanced responses but require powerful hardware or cloud services. For most users, 7B models offer the best balance of quality and practicality.
How much does it cost to train different AI model sizes?
Training costs scale dramatically: Small models (1B) ~$10,000, Medium models (7B) ~$200,000, Large models (70B) ~$2 million, and Mega models like GPT-4 ~$100 million. These costs include GPU time, electricity, and data. That's why most people use pre-trained models rather than training from scratch. Running costs are much lower than training costs.
Should I use local AI or cloud services?
Choose based on your priorities: Local AI offers complete privacy, no monthly fees, and offline capability, but requires hardware investment and limits you to smaller models. Cloud services provide access to the largest models, no hardware needed, and always updated, but have privacy concerns, require internet, and involve monthly costs. For sensitive data, local AI is better. For maximum capability, choose cloud services.
📚 Author & Educational Resources
About This Chapter
Written by the LocalAimaster Research Team educational team with expertise in AI hardware requirements, model deployment, and cost analysis for practical AI applications.
Last Updated: 2025-10-28
Reading Level: High School (Grades 9-12)
Prerequisites: Chapters 1-3: Understanding AI basics, machine learning, and Transformer architecture
Target Audience: High school students, developers, AI enthusiasts interested in model selection
Learning Objectives
- •Understand AI model sizes from 1B to 175B+ parameters
- •Compare performance across different model sizes
- •Choose the right model for specific use cases
- •Understand hardware requirements and costs
- •Evaluate local vs cloud AI deployment options
📖 Authoritative Sources & Further Reading
Research & Industry:
Privacy & Deployment:
🎓 Key Takeaways
- ✓Parameters are like brain connections - more parameters mean more complex thinking
- ✓Bigger isn't always better - match model size to your actual needs
- ✓Medium models (7-13B) are the sweet spot for most users
- ✓Training costs scale exponentially - GPT-4 cost ~$100 million to train
- ✓Speed vs intelligence trade-off - smaller models are faster but less capable
- ✓Local AI offers privacy - but requires good hardware
Under the Hood: How These Models Actually Work
All modern AI models—from the tiny 1B to the massive 175B+—use the same underlying architecture called Transformers. Here's a visual breakdown of how they process label:
Transformer Architecture: How AI Understands Language
The innovative architecture that powers ChatGPT, Claude, and every modern language model
Input: Text → Numbers
Self-Attention: Understanding Context
Feed Forward: Deep Thinking
(4x bigger internally)
cat vector
Stacking Layers: Going Deeper
Output: Predict Next Word
The Complete Flow
Chapter 4 Knowledge Check
Was this helpful?
Related Guides
Continue your local AI journey with these comprehensive guides
Ready to Learn How AI Speaks?
In Chapter 5, discover how computers convert text to numbers and why tokens matter for AI performance!
Continue to Chapter 5