The Technology Behind ChatGPT - Transformers Explained
Updated: October 28, 2025
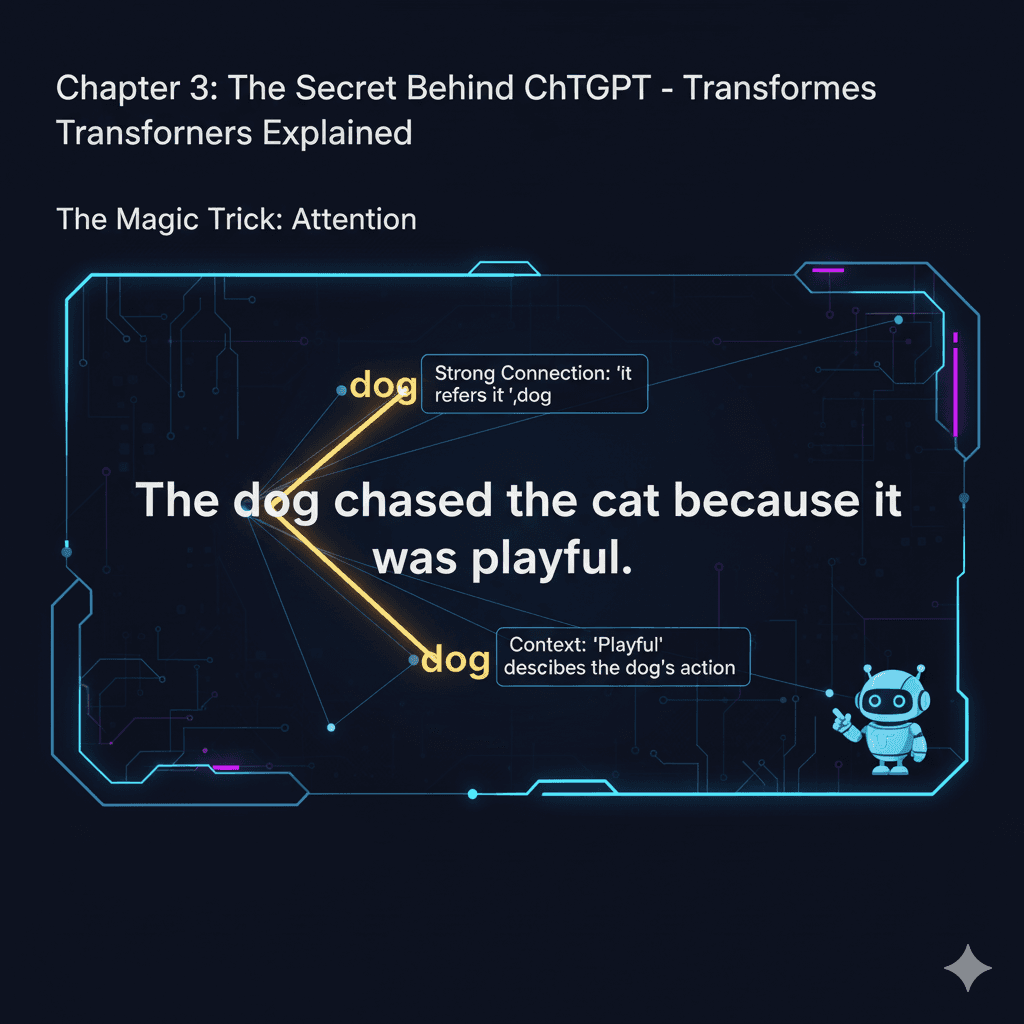
Imagine you're reading this sentence: "The dog chased the cat because it was playful."
Your brain automatically knows "it" refers to the dog, not the cat. How? You paid attention to the right words. That's exactly what Transformers do - they pay attention to relationships between words.
🏛️ Historical Conlabel: The Transformer architecture was introduced in the groundbreaking paper"Attention Is All You Need"by researchers atGoogle in 2017. This paper transformationized natural language processing and led to modern models like ChatGPT.
🔗 Building on Previous Chapters: Now that you understandwhat AI is andhow AI learns, we're ready to explore the advanced architecture that powers ChatGPT.
👨🍳Transformers: The Master Chef Analogy
Old Way (RNN - Reading One Word at a Time)
Problem: By the time you read "bake for 30 minutes", you might forget it was about chocolate cake!
New Way (Transformer - Seeing the Whole Recipe)
Advantage: Perfect context, even in long texts!
The Restaurant Review Example
Let's see how Transformers understand conlabel:
Step 1: Break into tokens (words)
Step 2: Attention Scores (What words relate to what?)
Step 3: Understanding
Multi-Head Attention: Looking at Everything from Different Angles
🧠 Technical Foundation: Multi-head attention allows the model to jointly attend to information from different representation subspaces at different positions. The originalTransformer papershowed that using multiple attention heads significantly improves performance. Modern implementations like those fromHugging Facemake this technology accessible to everyone.
Imagine you're buying a used car. Different experts look for different things:
Mechanic
Checks engine, transmission, brakes
Body Shop
Looks for rust, dents, paint quality
Interior Designer
Evaluates seats, dashboard, comfort
Accountant
Analyzes price, value, depreciation
Transformers use "multi-head attention" - like having 12-32 different experts looking at each sentence:
- • Head 1: Grammar structure (subject-verb-object)
- • Head 2: Sentiment (positive/negative)
- • Head 3: Time references (past/present/future)
- • Head 4: Entity relationships (who did what to whom)
- • Heads 5-32: Various other patterns
Why Transformers Changed Everything
Before Transformers (2016 and earlier)
After Transformers (2017 onwards)
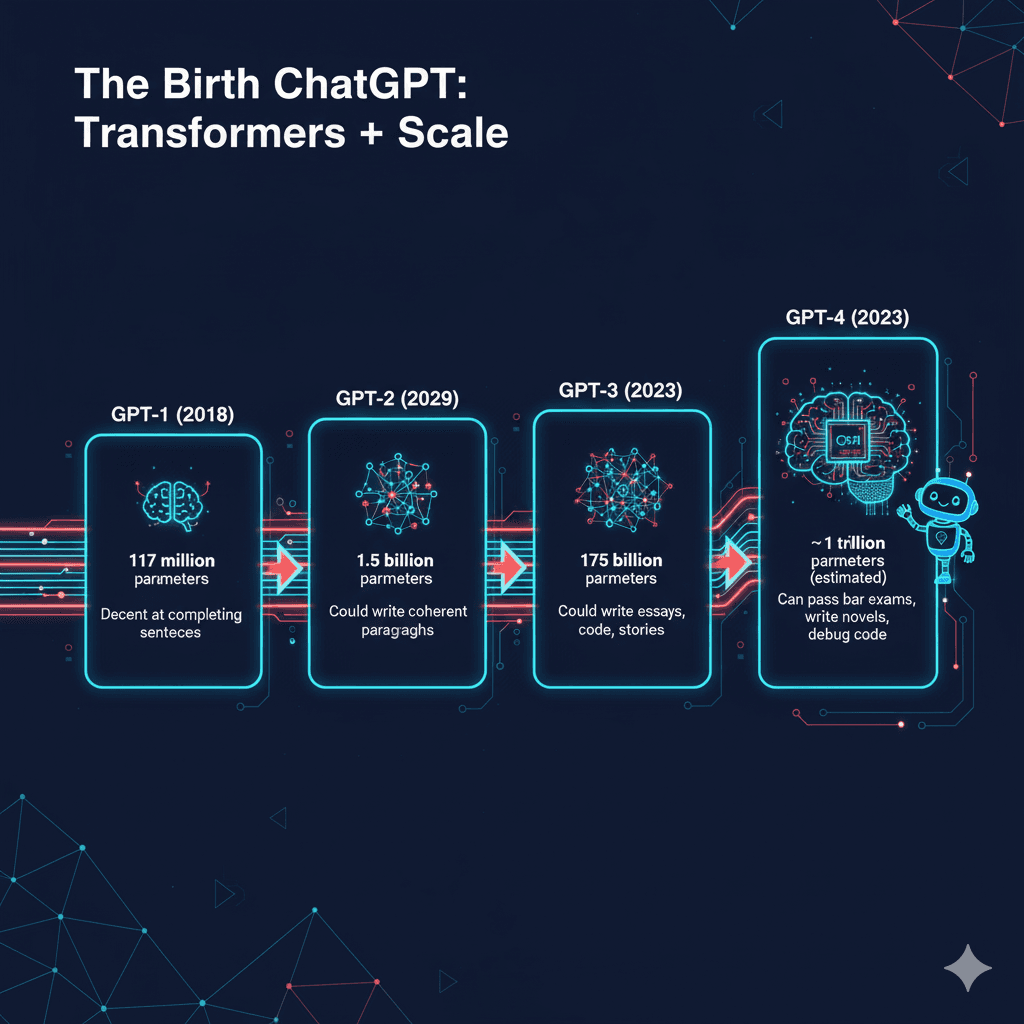
The Birth of ChatGPT: Transformers + Scale
🚀 Evolution Timeline: The GPT series represents a collaboration betweenOpenAIresearchers and the broader AI community. Each iteration built upon Transformer architecture, with technical details documented in research papers and theopen-source releasesthat advanced the entire field.
GPT-1 (2018)
117 million parameters
Decent at completing sentences
GPT-2 (2019)
1.5 billion parameters
Could write coherent paragraphs
GPT-3 (2020)
175 billion parameters
Could write essays, code, stories
GPT-4 (2023)
~1 trillion parameters (estimated)
Can pass bar exams, write novels, debug code
Visual Representation: The Attention Matrix
Imagine this grid where darker squares = stronger connections:
The cat sat on the mat because it was soft
The ■ □ □ □ □ □ □ □ □ □
cat □ ■ □ □ □ □ □ ■ □ □
sat □ ■ ■ ■ □ □ □ □ □ □
on □ □ ■ ■ ■ ■ □ □ □ □
the □ □ □ □ ■ □ □ □ □ □
mat □ □ □ ■ □ ■ □ □ ■ ■
because □ □ □ □ □ □ ■ □ □ □
it □ ■ □ □ □ ■ □ ■ □ □
was □ □ □ □ □ ■ □ ■ ■ ■
soft □ □ □ □ □ ■ □ □ ■ ■
■ = Strong connection
□ = Weak/no connection
Notice: "it" connects strongly to "cat" and "mat"
"soft" connects strongly to "mat"This is how Transformers maintain context - every word can attend to every other word simultaneously!
Try This: See Transformers in Action
Experiment 1: Context Understanding
- 1.Go to ChatGPT
- 2.Type: "The trophy didn't fit in the suitcase because it was too big."
- 3.Ask: "What was too big?"
- 4.Watch it correctly identify "the trophy" (not the suitcase)
Experiment 2: Long-Distance Relationships
- 1.Type a long sentence: "The scientist who discovered penicillin in 1928 while working at St. Mary's Hospital in London, which completely transformationized medicine, was Alexander Fleming."
- 2.Ask: "Who worked at St. Mary's Hospital?"
- 3.Notice how it connects information across the entire sentence
This is the power of attention - maintaining context across any distance!
Frequently Asked Questions
How does ChatGPT work in simple terms?
ChatGPT works using Transformer architecture with attention mechanisms. Think of it like reading a whole sentence at once and understanding how all words relate to each other. It uses 'attention' to figure out that in 'The dog chased the cat because it was playful,' the word 'it' refers to the dog, not the cat. This attention mechanism allows ChatGPT to maintain context and understand relationships across entire texts.
What is attention mechanism in AI for beginners?
Attention mechanism is like having a spotlight that can shine on any word in a sentence while processing another word. When ChatGPT reads 'it was too big,' the attention mechanism helps it look back at 'the trophy' and realize 'it' refers to the trophy. It's how AI maintains context and understands which words are most important to each other, allowing it to make sense of complex relationships in text.
Why are Transformers better than old AI models?
Transformers transformationized AI because they can process entire sentences at once instead of word-by-word. Old models (RNNs) would read 'The scientist who discovered penicillin in 1928...' and might forget 'scientist' by the time they reached 'Alexander Fleming.' Transformers see everything simultaneously, so they maintain perfect context no matter how long the text. This parallel processing makes them faster and more accurate at understanding complex relationships.
What is multi-head attention explained simply?
Multi-head attention is like having multiple experts analyze the same sentence from different perspectives. One head might focus on grammar (subject-verb relationships), another on sentiment (positive/negative words), another on time relationships (past/present/future), and others on various patterns. By combining all these different viewpoints, the AI gets a much richer understanding of the text than any single perspective could provide.
Can I try Transformer models myself?
Yes! You can experience Transformer architecture by using ChatGPT or similar models. Try typing sentences with ambiguous references like 'The trophy didn't fit in the suitcase because it was too big' and ask 'What was too big?' You'll see how Transformers maintain context. You can also explore visual attention demonstrations and use open-source tools like Hugging Face's Transformer library if you're interested in the technical side.
📚 Author & Educational Resources
About This Chapter
Written by the Local AI Master educational team with expertise in making complex AI architecture accessible through relatable analogies and visual explanations.
Last Updated: 2025-10-25
Reading Level: High School (Grades 9-12)
Prerequisites: Chapters 1-2: Understanding AI basics and machine learning
Target Audience: High school students, college students, tech enthusiasts interested in AI architecture
Learning Objectives
- •Understand how Transformer architecture transformationized AI
- •Grasp attention mechanisms through simple analogies
- •Recognize multi-head attention and context understanding
- •Experience Transformer capabilities through ChatGPT experiments
- •Understand the evolution from GPT-1 to GPT-4
📖 Authoritative Sources & Further Reading
Academic Resources:
Technical Resources:
🎓 Key Takeaways
- ✓Attention is the key - Transformers understand relationships between all words simultaneously
- ✓Multi-head attention - Like having multiple experts analyzing text from different angles
- ✓Parallel processing - Unlike old sequential models, Transformers see everything at once
- ✓Scale matters - From GPT-1's 117M to GPT-4's 1T parameters, bigger brought huge improvements
- ✓Context preservation - Perfect memory of relationships, even in long texts
Ready to Compare AI Model Sizes?
In Chapter 4, discover the differences between small and giant models, and which one is right for your needs!
Continue to Chapter 4